Overview
To optimize the value of data obtained from various disparate sources, organizations need a strategic lever to enable effective and efficient management of that data. Data virtualization within modern data architectures addresses the challenges of unifying data from multiple data sources by utilizing a logical data layer to securely connect and integrate authoritative enterprise data, standardize queries, and streamline availability. The Multiplatform Data Acquisition, Collection, and Analytics (MDACA) data fabric suite provides an enterprise logical data layer and manages the unified data for centralized access to enable organizations to realize the value of their data.
Background
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the generation of enormous amounts of data has become a norm. These data streams originate from diverse sources such as business transactions, medical records, financial activities, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sales and logistics data, and customer interactions. With exponentially growing data volume comes the challenges of managing data both strategically and effectively. It is crucial for businesses to adopt best practices and industry-standard data management approaches to maximize the potential of big data solutions. Among these solutions, Data Virtualization stands out as a technology enabler and solution accelerator that addresses the challenges of a growing big data ecosystem.
Key Challenges of a Big Data Ecosystem
Data Growth: As the volume of data increases, organizations must have a clear understanding of their data assets, their storage locations, and their value. Managing both structured and unstructured data becomes increasingly complex as data centers and databases expand over time.
Securing Data: Protecting large datasets from external threats is a significant challenge in the realm of big data. Delaying data security measures can expose valuable data to potential breaches and cyberattacks, making data protection a critical consideration.
Data Integration: The diverse sources, formats, and structures of data require organizations to establish relationships and connections between different data elements. While data integration is vital for effective analysis, reporting, and business intelligence, it often demands extensive management efforts.
Team Expertise in Technology and Skill Sets: Developing expertise within organizations to handle big data initiatives is difficult due to the ever-evolving technology landscape. Keeping up with changes in technology, cloud providers, and solution options poses a persistent challenge.
What is Data Virtualization?
Data virtualization offers a modern approach to data integration, minimizing the need for multiple persistent data stores and associated costs. It acts as a logical data layer that integrates enterprise data from a non-replicated, single source of truth, providing real-time information to business users. Key features of the logical layer include:
Conceal Complex Technology: By abstracting the underlying complexities, users and applications interact with a user-friendly interface while remaining unaware of the technical details.
Standardize Queries: Instead of tailoring queries for different underlying databases, data scientists, developers, and analysts can leverage standardized queries, simplifying the data access process.
Connect: Data virtualization enables linking of data across disparate systems, including cloud applications, data warehouses, repositories, and data marts. The data remains connected, eliminating the need for data duplication and transfer between environments.
Integrate/Federate: Regardless of format, latency, or location, data is logically integrated into a unified view. Complex tasks such as data transformations and abstraction are hidden from end-users, allowing seamless data access.
Security: Data virtualization ensures data is secured through a centralized location integrated with enterprise identity management solutions, enhancing overall protection of data at rest and data in-transit.
Accessibility: By providing a centralized and managed mechanism to view enterprise data, Data virtualization enables easy and secure data access, facilitating faster and informed decision-making.
ETL vs. Data Virtualization
While Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) tools have traditionally been used for data integration and migration, data virtualization offers enhanced capabilities. Here are the key distinctions between ETL and data virtualization:
Extract – Transform – Load: ETL involves extracting data from various sources, transforming it to meet specific requirements, and loading it into a central data environment. Data cleansing, validation, and other transformations are performed before the data becomes accessible to users. ETL is suitable for permanently migrating legacy data into a new environment.
Data Virtualization: Data virtualization provides a logical data layer that integrates disparate data sources in real-time, without the need for data duplication. It offers a unified view of the data, concealing complexities and delivering immediate insights to users.
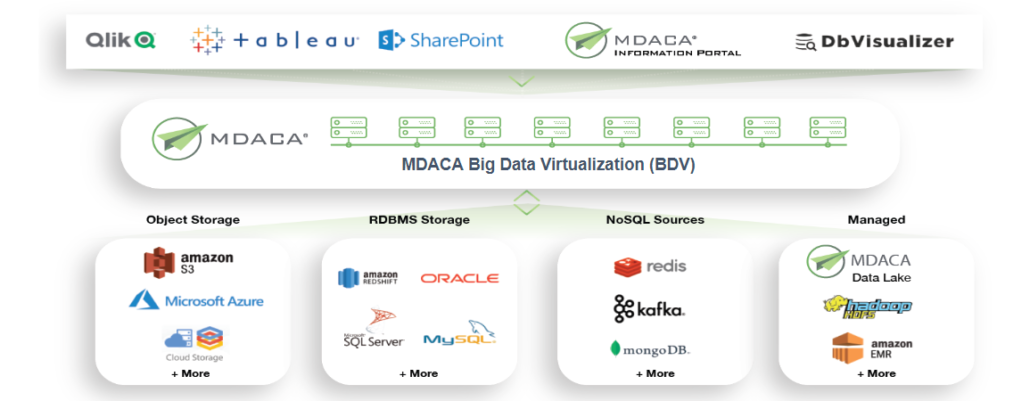
How MDACA Elevates Performance with Big Data Virtualization
MDACA’s Big Data Virtualization (BDV) platform empowers businesses by reducing costs and boosting productivity. By minimizing the need for data duplication and by breaking down data silos, MDACA’s BDV cuts development and resource costs. Providing real-time access to data eliminates downtime and increases user productivity. Furthermore, MDACA BDV supports system modernization by seamlessly integrating with legacy systems and applications, ensuring minimal disruption and ease of adoption for users.
In the era of big data, businesses must embrace innovative solutions to harness the full potential of their data assets. By adopting MDACA Big Data Virtualization, organizations can achieve proper data management, centralized security, and real-time information availability for informed decision-making.