The MDACA Synthetic Data Engine (SDE) was designed to seamlessly access and create meaningful, intelligent synthetic data without compromising the privacy of corresponding sensitive, real data. The MDACA SDE creates non-reversible, artificially generated data with the statistical characteristics and correlations of the real data.
What is Synthetic Data?
Synthetic data is non-reversible, artificially generated data that replicates the statistical characteristics and correlations of real-world, private data.
While protecting the privacy of corresponding real data without disclosure, synthetic data may be used as test data to support:
- Software development lifecycle, especially during testing
- Compliance with data sharing restrictions and regulatory requirements such as Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and Sarbanes Oxley Act
- Training advanced Machine Learning (ML) models and running simulations
- Acceleration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) / ML projects with large data sets that are very “close” to the real data
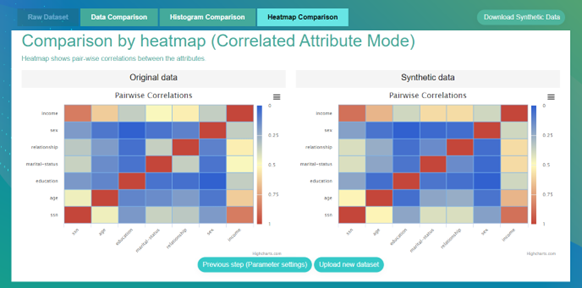
MDACA Synthetic Data Engine provides data comparison, histogram comparison, and heatmap comparison of the distribution and attribute correlation measures between the synthetic and real datasets for users to have confidence in accuracy of the generated data.
Why Use Synthetic Data?
While data de-identification provides a degree of protection against disclosure of sensitive data, it may not fully protect data from re-identification because there are other sources of data that still contain identifying information. Data anonymization is a stronger form of data minimization technique with higher levels of data privacy that completely and permanently removes the sensitive information (e.g., personally identifiable information, protected health information).
MDACA SDE supports privacy and safeguards against reverse engineering when synthetic data sets are derived from real data, providing both utility and privacy.
- To maximize utility, data synthesis must preserve to a high degree the statistical properties and structure of the original dataset; this creates both intelligent data, as well as meaningful data.
- To maximize privacy, data synthesis must satisfy the definition of differential privacy that makes it impossible to tell whether a particular individual was part of the original dataset.
An ideal synthetic data set optimizes both utility and privacy; however, acceptable tradeoff points are common.
Time to Market
Accelerate time to market by providing highly relevant test data for Development Security Operations (DevSecOps) processes within the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
Cost Effective
The MDACA Synthetic Data Engine is designed to eliminate redundant data storage by enabling on-demand or ‘just-in-time” generation to reduce costs by masking synthetic data creation via a user-friendly interface.
Benefits of Synthetic Data Engine
The MDACA Synthetic Data Engine protects PII and PHI data and provides meaningful data in support of AI/ML model development and application testing, minimizing data duplication and meeting business needs.
Designed to provide strong privacy guarantees while minimizing the complexities associated with understanding the processes for generating synthetic data that is structurally and statistically similar to the sensitive, real data.
A web-based component of the integrated MDACA suite of applications enabling increased confidence and trust in use of synthetic data for research, software development, testing, and other activities while safeguarding corresponding real data.
Accuracy of synthetic data is essential to Machine Learning models to ensure the algorithms are trained consistently for use with the anticipated real data. Data needs to simulate/adhere to patterns in order to develop and train the models to increase the accuracy of the model development. MDACA creates intelligent synthetic data with high statistical relevance to the underlying real data, providing ML models with accurate input for training the algorithms.
Preserve against disclosure of the corresponding real data with the capability to create intelligent, meaningful synthetic data. Enable users to access enterprise data stores – while concealing the technical complexities of database types and data locations – within a controlled pipeline to generate synthetic data on-demand without data movement or replication.