Jim Martin
Business Dev Director
SpinSys
Kaitlyn Hickman
Project Analyst
SpinSys
Introduction
Whether you are in the software industry, healthcare, finance, agriculture or almost anything else, chances are you are benefiting from the use of what is known as “Big Data.” But what is Big Data? According to Gartner’s definition, it is “data that contains greater variety arriving in increasing volumes and with ever-higher velocity.” The amount of data being created every day continues to grow at an exponential rate, and businesses are trying to figure out ways to process and utilize it in a manageable way in order to maximize the value of their data.
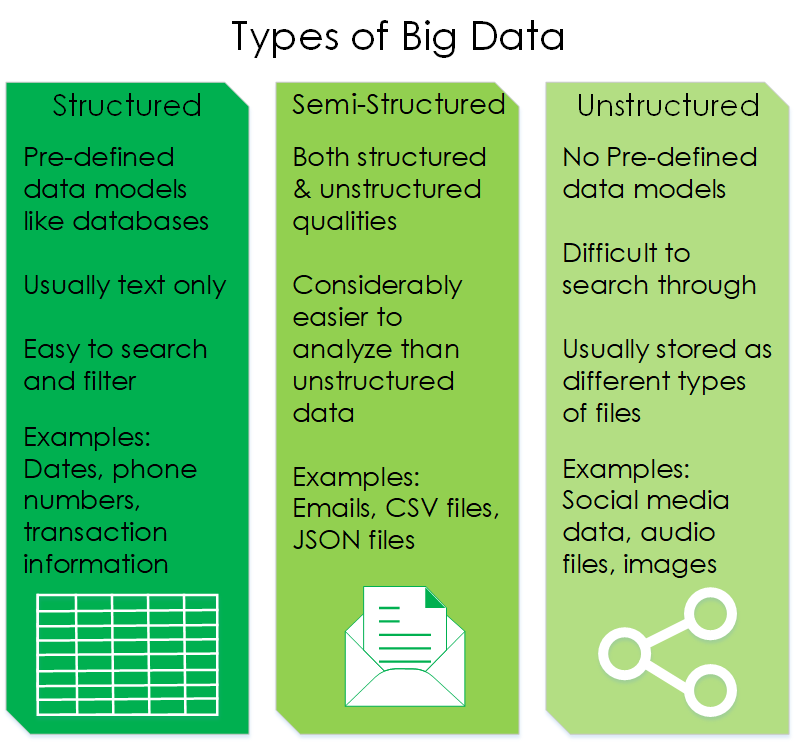
Types of Big Data
Structured: This type of data adheres to a predefined data model and is easier to analyze. Structured data typically comes in the form of numbers or text in formats that are familiar, such as Excel files or SQL databases. Each of these have structured rows and columns that can be sorted.
Unstructured: This type of data has no data model and is stored in its native file format that will require processing to be utilized. Currently, the amount of unstructured data outnumbers structured data significantly and continues to grow at a rapid pace. Examples of unstructured data include data from social media, word documents, or things like PDFs. (submission form with medical data/word docs/pdfs that are non-database based)
Semi-structured: Unsurprisingly, this third type of Big Data falls in between structured and unstructured. This type of data has a defined structure to it, but doesn’t fit into the standard forms we already have so it will still require some type of processing. A familiar example would be emails, they can be sorted by sent, received, and drafts, but the data within the emails is unstructured.
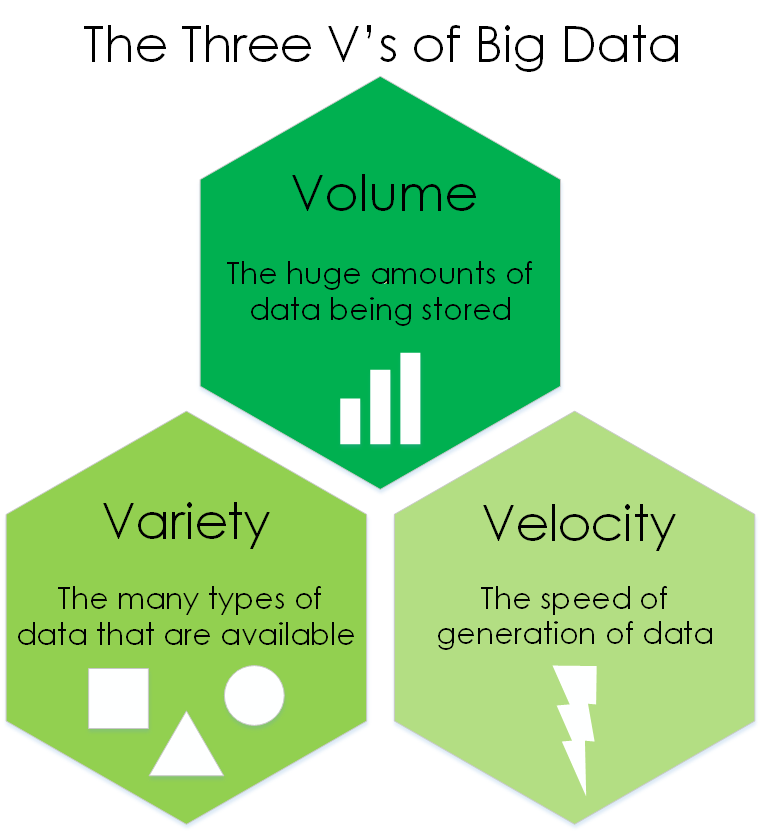
There are three main characteristics when it comes to talking Big Data: volume, variety, and velocity. Each of these play a significant role in how big data is handled and ultimately how it is used by businesses.
Volume: Simply put, the volume of Big Data is the amount of data that is being created and collected from numerous sources. The volume of data being stored needs to be considered as this size can grow to enormous quantities very quickly. Having the right amount of space to store that data, whether in a data lake or in the cloud, is extremely important.
Variety: The sources of Big Data can be vast and the file formats can vary greatly, which leads to a wide variety of data types. Depending on the industry, businesses can be collecting data from numerous sources in a wide range of file types. This leads to a large variety in the data collection process.
Velocity: With such significant volumes of data being gathered, it has to be collected quickly and processed just as fast so companies can make use of all that information in a timely manner. Unstructured and semistructured data types typically require additional processing to provide helpful information.
Additional V’s
As Big Data continues to grow and more and more businesses are learning to manage it, additional V’s have begun to emerge: Veracity, Variability, and Value. Veracity is the degree to which big data can be trusted, it’s the quality of the data that you are collecting and managing. Variability is the way in which Big Data can be used and formatted. There are so many different ways to use the massive amounts of data that exist so variability has started to come into focus. Value is the final V and it is exactly that, the business value of the data collected. So much information can be captured from Big Data that the value of it continues to grow and businesses can capitalize on it and use the information to make better decisions.
Big Data Benefits
So all of this information is being generated and collected at unprecedented speeds, but what does all of that data actually provide to businesses? Data has become extremely valuable and is now constantly being analyzed to look for opportunities to optimize processes, improve product performance, or increase customer satisfaction. As big data technologies continue to evolve coupled with a significant decrease in data storage allows companies to hold on to more and more information that can help influence business decisions and drive profits. The more data that is collected and analyzed by businesses, the more opportunities become available for valuable insights that lead to innovative solutions.
How MDACA Supports Big Data Initiatives
MDACA (Multi-Platform Data Acquisition, Collection and Analytics) is a secure, unified data platform for gaining real-time access to your enterprise-wide data assets, irrespective of its location and format. MDACA provides easy data configuration and integration with existing systems for easier big data management. This cloud ready platform can move high volumes of data between relational databases, file systems and data stores whether on-premise or in the cloud while reducing cost.
MDACA Areas of Focus
There are three main capabilities of the MDACA platform that work together to provide enhanced insight and control over your information by connecting data from a wide range of locations. Data collection, data storage and data access and analytics combine to help you manage big data and provide meaningful insights that your business desires.
Data collection and integration gives you enhanced insight and control by connecting all of that collected data from multiple sources. This allows for real time migration and continuous integration of structured and unstructured data.
Data Storage with the MDACA Cloud-Native Data Lake maximizes performance and takes advantage of the flexible storage and elastic processing benefits offered by the Cloud. Instead of relying on rigid data warehouses, organizations can now store data in an optimized, compressed, and cost-effective manner that is securely and easily available to each system. Securing cloud data is just as important as effectively storing and organizing it.
Data Access and Analytics is a top priority with MDACA which provides big data virtualization, cloud storage explorer that allows for management of files across multiple cloud storage providers, and data export services to export data and generate reports as needed.
Conclusion
Overall, Big Data sounds like a big mysterious concept, when in reality it can easily be identified with different types of data and the way that it is stored, created, and analyzed. Structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data are all types of information we are familiar with, but the significant volume of it all can be overwhelming, leaving users wondering where to start and how to handle it. Having proper systems in place and following industry best practices when handling Big Data will help solve a variety of problems leading to a more successful business.