Kenna Harris
Project Analyst
SpinSys
Introduction
Enormous amounts of data are being generated every second, deriving from a multitude of transactions and activities including business transactions, medical transactions, financial transactions, Internet Of Things (IOT), sales activities, logistics activities and customer activities. With data creation occurring at an exponential rate, it is imperative to recognize the importance of data as a valuable intellectual asset and the fuel driving companies. However, with big data comes big responsibility and as data continues to grow it must be appropriately and strategically managed through best practices that are recognized industry-wide and as a critical component within business models. As improved data collection methods and enhanced data storage products continue to emerge, business leaders must remain aware of emerging big data solutions and their respective benefits. Data Virtualization is a big data solution approach that provides capabilities to support growth challenges within a big data ecosystem.
Key Challenges of a Big Data Ecosystem
Data Virtualization is capable of addressing and supporting key challenges within a big data ecosystem, including the following:
Data Growth: As data continues to grow, it must be properly stored and managed by knowing what data you have, where the data is stored, and the value of the data. Furthermore, data centers and databases, where data is typically housed, continue to grow exponentially over time and further increase the complexities of data storage. Organizations additionally need to be able to manage both structured and unstructured data.
Securing Data: Securing large sets of data is a daunting challenge of Big Data. It is critical to ensure data security is not delayed to later stages, as unprotected data can become an open door invitation for malicious hackers.
Data Integration: Data comes from a wide range of sources and in a variety of formats and structures, requiring organizations to identify and determine relationships between data. Although data integration requires a high level of management efforts, it plays a crucial role for analysis, reporting and business intelligence.
Team Expertise in Technology and Skill Sets: Developing in-house expertise in support of Big Data initiatives is a pervasive challenge due to changes in technologies and an increase in the number of cloud providers and solution options.
What is Big Data Virtualization?
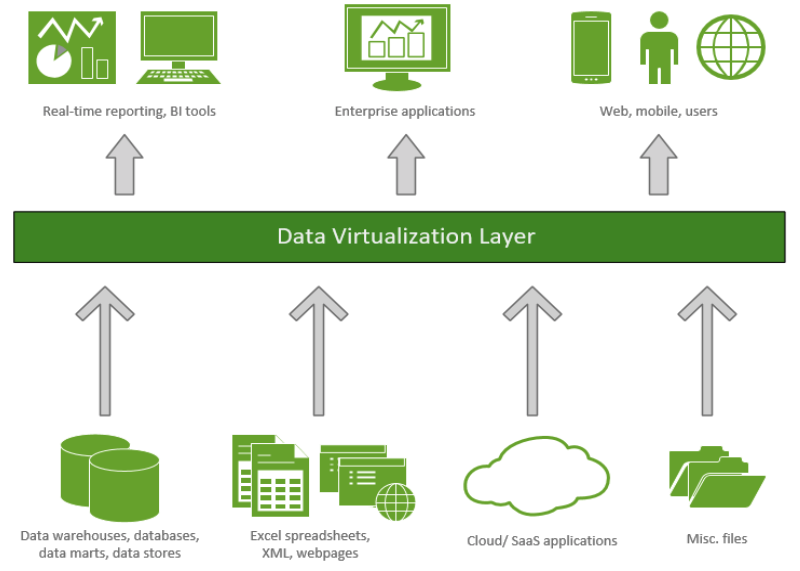
Big Data Virtualization offers a modernized approach to data integration while minimizing persistent data stores and associated costs. It serves as a logical data layer that combines all enterprise data to produce real-time information for business users. Core features of the logical layer include the ability to:
Conceal Complex Technology: By leveraging a logical layer to access data, users and applications only interact with the user-friendly interface of the BDV. The logical layer serves as a mask so that the complexities occuring behind the scenes remain undisclosed to the user.
Standardize Queries: Data scientists, database developers and application developers can leverage standardized queries, rather than having to tailor multiple queries to the underlying databases.
Connect: Enterprise data across disparate systems are linked together, including data stored within enterprise cloud applications, data warehouses, repositories, data marts, etc. Linked data is not copied into another environment. Data is connected, not replicated; therefore data copies are not being created and migrated into another environment.
Integrate/Federate: Data is logically integrated together, regardless of format, latency, or location. Logical processors are constructed to perform a number of complex tasks, including data transformations and data abstraction. As previously stated, the technical complexities performed at this level remain completely hidden from end users via the logical layer.
Security: Data is secured through one centralized location that is integrated with enterprise identity management solutions.
Accessibility: By providing a single, centralized, managed, and secure mechanism to view enterprise data, users can easily access and understand the information being delivered.
Figure 1: Big Data Virtualization Process Diagram
ETL vs. Big Data Virtualization
The enhanced capabilities of data virtualization are derived from a plethora of concepts, including the traditional methods of Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) tools. While ETL methods provide an appropriate solution to permanently migrate legacy data into a modernized environment, the following breakdown distinguishes key differences between ETL and data virtualization.
Extract – Transform – Load: ETL involves initially extracting data from various sources through an extraction tool and preparing it accordingly to be properly loaded into a central hosting environment (e.g., data warehouse, operational data store, data lake, data marts). Data transformations are performed by big data tools to meet specific data requirements prior to loading. To meet the specified requisites, big data tools are designed to execute specific tasks, including data cleansing, data validation, schema conversions, translations of coded values, and more. After data transformation is completed, the data is staged and loaded into the central hosting environment where it is then available for user accessibility.
Big Data Virtualization: As previously discussed, data virtualization consists of providing a logical data layer and integrating disparate data together to deliver comprehensive information to business users. Unlike ETL, data virtualization unifies and delivers data into a single platform without ever duplicating or moving data into another environment. Data virtualization additionally provides users with real-time data, while ETL is limited to providing temporal data based on automated refresh rates.
How MDACA Elevates Performance with Big Data Virtualization
By implementing a service that offers big data virtualization, such as the MDACA Big Data Virtualization (BDV) platform, extraneous costs are cut and business productivity soars. Development and resource costs are diminished as a direct result of the reduction in data copies and need for data silos. By providing users with data in real-time, downtime is eliminated to create more time and enhance user productivity. Furthermore, outdated data architecture can be upgraded and modernized with minimized risk. Our Multiplatform Data Acquisition, Collection, and Analytics (MDACA) BDV is intentionally designed to support system modernization, as legacy systems and business applications are replaced and updated with minimal disruption to users.
Along with our BDV solution, MDACA is capable of providing additional services to help you enhance your data management strategies. Our MDACA big data solutions are uniquely designed to help your organization enhance your data collection and data storage tools, while simultaneously increasing data accessibility enterprise-wide to generate meaningful insights for data driven decisions.
Conclusion
All in all, it is critical for businesses to continue embracing and adopting innovative data solutions that maximize the value of data into a powerful asset. With MDACA Big Data Virtualization, organizations are empowered to enforce proper data management, implement centralized security, and provide users with real-time information to make faster and more informed decisions.